Toolkit Tasks
Toolkit task 1
Things I already Know
Things I already Know
- Paint using Acrylic,Watercolour,Oil etc...
- Draw/Sketch use pencil/pen/markers/chalk/Ink/Charcoal
- How to use a Camera/photograph
- Stop-Motion animation/Claymation/Whiteboard animation
- Story-board/Research art and some Art history
- IMovie
- shot/camera angles
- A bit of photoshop and Illustrator
- Screenprint
- camera shot angles/lighting
- still life
- life drawing
- making puppets out of wire, clay, tights, fingerpuppets, voodoo dolls, sockpuppets,hand puppets newspaper out of a balloon and paper mache
- making dolls
- making marrieriottes
Things I wanna learn
- Lino print
- Printmaking
- 3 colour lino printing
- Collagraphs
- How to use photoshop properly
- How to use a camera and Digital SLR properly
- How to use premiere pro and learn how to set Audio and adjust music, the basic set up in première pro to start editing films and Learn more on montage layering and just collage and laying itself
- / After Effects Making a reel for film, Applying photographic skill like taking picture before hand to make a film on after effect and 3D effects which to the light on the texts more on moving image
- /Illustrator
- use Lighting camera angles properly
- How to make better stop-motion animations better and just better animations in general
- Developing films in darkroom properly and use different methods
- use different programs
- sound and add different sounds and effects together properly
Film is considered as an art industry.Films described to be a story or event recorded by a camera as a set of moving images which can be shown in a cinema or television. Film can also be a flexible strip of plastic or other material in the form of very thin flexible sheet. Film is coated with a light sensitive emulsion for exposure in a camera and is used to produce photographs and motion pictures.

Plastic Film is a thin continuous polymeric material. Thicker plastic material is often called a “sheet”. These thin Plastic membranes are used to separate areas or volumes, to hold items, to act as barriers, or as printable surfaces.Plastic films are used in a wide variety of applications. These include: Packaging, plastic bags, labels, building construction, landscaping, electrical fabrication, photographic film, film stock for movies,video tape, etc....
 Films were originally recorded onto plastic film which was shown through a movie projector projector onto a large screen (in other words, an analog recording process). The adoption of CGI-based special effects led to the use of digital intermediates .
Films were originally recorded onto plastic film which was shown through a movie projector projector onto a large screen (in other words, an analog recording process). The adoption of CGI-based special effects led to the use of digital intermediates .Most contemporary films are now fully digital through the entire process of production, distribution, and exhibition from start to finish. Films recorded in analog form traditionally included an optical soundtrack , which is a graphic recording of the spoken words, music and other sounds that are to accompany the images.
It runs along a portion of the film exclusively reserved for it and is not projected.
Films are cultural artifacts created by specific cultures They reflect those cultures, and, in turn, affect them. Film is considered to be an important art form, a source of popular entertainment, and a powerful medium for educating —or indrodoctrinating —citizens. The visual basis of film gives it a universal power of communication.
Some films have become popular worldwide attractions by using dubbing or subtitles to translate the dialog into the language of the viewer. Some have criticized the film industry's glorification of violence and its sexist treatment of women.
Some films have become popular worldwide attractions by using dubbing or subtitles to translate the dialog into the language of the viewer. Some have criticized the film industry's glorification of violence and its sexist treatment of women.
 The individual images that make up a film are called frames . During projection of traditional films, a rotating shutter causes intervals of darkness as each frame in turn is moved into position to be projected, but the viewer does not notice the interruptions because of an effect known as persistence of vision, whereby the eye retains a visual image for a fraction of a second after the source has been removed. The perception of motion is due to a psychological effect called Phi phenomenon
The individual images that make up a film are called frames . During projection of traditional films, a rotating shutter causes intervals of darkness as each frame in turn is moved into position to be projected, but the viewer does not notice the interruptions because of an effect known as persistence of vision, whereby the eye retains a visual image for a fraction of a second after the source has been removed. The perception of motion is due to a psychological effect called Phi phenomenon  This optical illusion causes the audience to perceive continuous motion between separate objects viewed rapidly in succession. A film is created by Photographing actual scenes with a motion Picture camera ; by photographing drawings or miniature models using traditional animation techniques; by means of CGI and computer animation; or by a combination of some or all of these techniques and other visual effects .
This optical illusion causes the audience to perceive continuous motion between separate objects viewed rapidly in succession. A film is created by Photographing actual scenes with a motion Picture camera ; by photographing drawings or miniature models using traditional animation techniques; by means of CGI and computer animation; or by a combination of some or all of these techniques and other visual effects .
The word "cinema" is often used to refer to the industry of films and filmmaking or to the art of filmmaking itself. The contemporary definition of cinema is the art of simulating experiences to communicate ideas, stories, perceptions, feelings, beauty or atmosphere by the means of recorded or programmed moving images along with other sensory stimulations
 The name "film" originates from the fact that Photographic film (also called film stock ) has historically been the medium for recording and displaying motion pictures. Many other terms exist for an individual motion picture, including picture, picture show, moving picture, photoplay and flick. The most common term in the United States is movie, while in Europe film is preferred. Terms for the field in general include the big screen, the silver screen, the movies and cinema; the latter is commonly used in scholarly texts and critical essays, especially by European writers. In early years, the word sheet was sometimes used instead of screen.
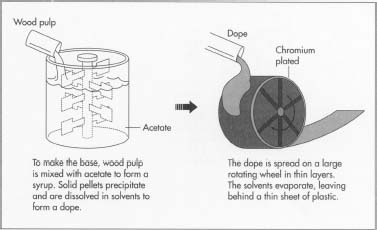
The name "film" originates from the fact that Photographic film (also called film stock ) has historically been the medium for recording and displaying motion pictures. Many other terms exist for an individual motion picture, including picture, picture show, moving picture, photoplay and flick. The most common term in the United States is movie, while in Europe film is preferred. Terms for the field in general include the big screen, the silver screen, the movies and cinema; the latter is commonly used in scholarly texts and critical essays, especially by European writers. In early years, the word sheet was sometimes used instead of screen.8 process methods to make a plastic film
Plastic films are usually thermoplastics and are formed by melting for forming the film.
1.Cast it by using plastic extrusion where a high-volume manufacturing process in which raw plastic is melted and formed into a continuous profile.It then becomes a cast film which is cooled or quenched then wound up on a roll.
2. Extruded where film can be stretched, thinned, or oriented in one or two directions. blown or tubular process forces air into an extruded ring to expand the film. Flat tenter lines stretch the extruded film before annealing.
3. Calender rolls can be used to form film from hot polymers
4. Solution deposition is another film forming process.
5. Skiving is used to scrape off a film from a solid core (sometimes used to make PTFE thread seal tape)
6.Coextrusion involves extruding two or more layers of dissimilar polymers into a single film 7.Lamination combines two or more films (or other materials) into a sandwich
8.Extrusion coating is used to form a film into another film or substrate
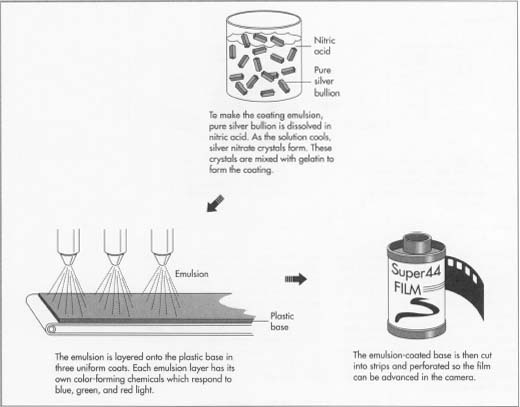
Photographic film
is film that is chemically reactive material that records a fixed or still image when the film is exposed to light.
How a photographic film is made
1. Place the film in a camera, then allow light from the image being photographed to enter you can also focus it by making it larger or smaller by the camera lens
2. You then make the film exposed to the image by opening a shutter in the camera body, and the combination of the speed of the shutter and the film speed (which is the chemical reactivity of the film) controls and allowing the amount of light to strike the film.
3. Then allow the image to be recorded on the film, but it has to be a latent or invisible image.Then when the film is removed from the camera, it has to be developed by chemical processes into a visible image.
4.The visible image has to be negative or the reverse in brightness of the way our eyes see light; the brightest parts of the photographed object appear the darkest on the negative where the film received the most exposure to light.
5. The negative image is then made positive, or as our eyes see it, by another type of processing whereby the negative is printed on sensitive paper. Color-reversal films are positives and are used for making slides. All of the elements of the process—the parts of the camera, the type and parts of the lens, the type of film, including its chemistry, the developing process, the printing process, and the type of paper—contribute to the sharpness or trueness of the finished photograph.
another way to make a film strip is by using photoshop here is a link and tutorial on how to do it. http://photoshopcafe.com/tutorials/filmstrip/filmstrip.htm
Film Terminology
Film Techniques
Continuity Suggests continuous action with respect to angles, props and positioning of actors
Cut Instant change between frames
Mix/Dissolve Image on screen appears to dissolve/fade away while another scene is appearing; originally done by overlaying
several frames when splicing celluloid
Superimposition Similar to mix but lasts for longer so both shots are actually visible at once
Fade in/Fade out Image fades into blackness before the next appears or a scene emerges from blackness
Wipe One scene pushes another off the screen sideways, in order to replace it
Matched cut:Shows Familiar relationship between shots making the change smoother
Jump cut: This is when two sequential shots of the same subject are taken from camera positions.
Motivated cut:This is a cut made at the point where something has occured. This makes the viewer immediately want to see something not currently visible
Film movement
Regular speed 24 frames per second Gives a sense of reality
Slow motion Filmed at a faster rate than 24 frames per second but
played back at regular speed
Gives the effect of slow motion when played at normal
speed; gives a sense that time is suspended; creates
tension, excitement, romance
Fast motion Pictures taken at very high speeds (128 frames per
second or more)
Movement is speeded up; creates tension, excitement,
anxiety, comedy
Film/shot angles types
Close-Up
This is a shot showing a small amount of a scene such as the characters face, head and shoulders and reveals the facial expression and emotion of the character.Aso A detailed view of a person or object. A framing in which the scale of the object shown is reluctantly
large. In a close-up a person’s head, or some other similarly sized object, would fill the frame.Like in this picture from the film The Shining
Extreme Close-up
Medium shot

 Medium shot is where half of the figures body is cut off showing it only up to the waistline and features above.from the waist-up.
Medium shot is where half of the figures body is cut off showing it only up to the waistline and features above.from the waist-up.

Medium Long shot:Shows the figure from head to chest.Framing such than an object four or five feet high would fill most of the screen vertically. Also called plain américain, given its recurrence in the Western genre, where it was important to keep a cowboy’s weapon in the image.
two shot:Shows two people in medium-long shot to show conversations
Medium close-up:A relatively close shot, revealing the human figure from the waist up.
establishing shot:Places the characters and action in a context. It's also an opening scene a sequence used to set the scene

Long Shot: A long shot Shows the whole subject, with room to spare at the top and bottom of the frame
over the shoulder:A kind of two-shot where the camera views the scene from behind one character’s shoulder; creates some tension
and a sense of expectation
point of view: Shows a scene from a particular character’s viewpoint; the viewer becomes that character.Also
shot taken with the camera placed approximately where the character’s eyes would be, showing what the character would see; usually cut in before or after a shot of the character looking. Horror films and thrillers often use POV shots to suggest a menacing and unseen presence in the scene.


Reaction shot:A shot to show an emotional response to the immediately preceding action or words of another character in the scene, or to an event in the immediately preceding scene which may or may not involve another actor (e.g., an explosion, monster, empty room, etc.)
 Camera Angles
Camera Angles
Eye-level shot Camera is set horizontal to the subject it gives off a Realistic, usual shot effect
Low-angle shot Camera is below the subject, looking up Makes characters appear larger, more imposing,threatening
High-angle shot Camera looks down on the subject Makes character vulnerable, insignificant or small
Bird’s eye view/overhead Camera is at an extreme high angle Shows an overall view of the situation
In order to have a great quality image when photographing with a camera these are some camera focus techniques used
Crane shot:A shot taken from a mechanical device called a crane which can carry the camera in any direction
Panning Camera support remains fixed while camera moves from side to side (horizontally)
 Handheld Camera is not on a steady support; gives a sense of action or uneasiness; increases intensity
Handheld Camera is not on a steady support; gives a sense of action or uneasiness; increases intensity
Tool Kit Task 3
Even though this is on my practical task It is also a toolkit task showing how I've made it and what I've used to create it and the different stages.
Lighting definition
Lighting is a deliberate use of light to achieve a practical or aesthetic effect.It uses both artificial light sources e.g. lamps and light fixture.As well as natural illumination by capturing daylight.
there are many types of different lighting techniques like
 Low-intensity lighting and haze which is used at concerts and in concert hall allows laser effects to be visible.
Low-intensity lighting and haze which is used at concerts and in concert hall allows laser effects to be visible.
 Task Lighting
Task Lighting
used for concentrated purposes like reading or inspecting materials.
Accent lighting
 decorative, intended to highlight pictures, plants or or other elements of interior design and landscaping
decorative, intended to highlight pictures, plants or or other elements of interior design and landscaping
General lighting ( ambient light) fills in between the two and is intended for general illumination of an area. e.g. lamp on a table or floor, or a ceiling
Down-lighting Uses fixtures on or recessed in the ceiling casting light downward. This tends to be the e.g. in both offices and homes
Front lighting makes the subject look flat as its casts almost no visible shadows.
UPlighting Used to bounce indirect light off the ceiling and back down.
Daytime/natural lighting
This uses windows, skylights or light shelves which can be used as the main source of light during daytime in buildings. This can save energy in place of using artificial lighting, which represents a major component of energy consumption in buildings.
Proper lighting can also be used to enhance task performance, improve the appearance of an area, or have positive psychological effects on occupants.
Indoor lighting is usually accomplished using light fixtures and is a key part of interior design Lighting can also be an intrinsic component of landscape projects. Examples of indoor lighting
wall mounted light with shadows


fluorescent,
LED light strip/ LED
Rope
Neon are all forms of background lighting.
 Recessed which is can or pot lights mounted on a ceiling
Recessed which is can or pot lights mounted on a ceiling
 Track is low voltage and decorative lighting aimed at the wall
Track is low voltage and decorative lighting aimed at the wall
 Soffit lighting close to wall lighting can be general or a decorative wall-wash, used to bring out texture on walls
Soffit lighting close to wall lighting can be general or a decorative wall-wash, used to bring out texture on walls
 Animation fountain
Animation fountain
OutDoor lighting examples
 High mast lights
High mast lights
 Street lamps .
Street lamps .
Flood Lights
 Beacon lights, security and
Beacon lights, security and  entry lights and underwater
entry lights and underwater

 accent light
accent light
For Vehicles: Headlights
Light exposure techniques and effects
Exposure Correct exposure: image appears normal
Over-exposure: image appears whiter owing to more light
Under-exposure: image appears darker
Source Natural, for example, real daylight from the sun
Artificial light effects are created using lighting equipment
Direction
this uses top,bottom,front, back and side direction effects
Top: the subject appears angelic, innocent, good
Bottom: conveys sinister nature of subject
Front: neutral
Back: the subject is silhouetted; appears threatening; can produce halo effect
Side: there is a contrast between lit and unlit sides; the subject can appear untrustworthy
high-key lighting Fully lit, generally bright-looking scene; no shadows; often used in comedies and romances
Low-key lighting Partially lit scene; lots of shadow; creates feelings of suspense or sensuality
key lighting
 is the first and usually most important light that a photographer, cinematographer, lighting cameraman, or other scene composer will use in a lighting setup. The purpose of the key light is to highlight the form and dimension of the subject. The key light is not a rigid requirement; omitting the key light can result in a silhouette effect. Many key lights may be placed in a scene to illuminate a moving subject at opportune moments.
is the first and usually most important light that a photographer, cinematographer, lighting cameraman, or other scene composer will use in a lighting setup. The purpose of the key light is to highlight the form and dimension of the subject. The key light is not a rigid requirement; omitting the key light can result in a silhouette effect. Many key lights may be placed in a scene to illuminate a moving subject at opportune moments.
This is a typical three point setup with a shoulder or back-side lamp to create contrast between the background and center object so as to give a three-dimensional appearance In the image it starts off with a key light then fill light which is This is the secondary light and is placed on the opposite side of the key light. It is used to fill the shadows created by the key.And lastly a backlight is placed behind the subject and lights this is used to provide definition and highlights around the subject's outlines.
Colour
Term Colour Effect Case study
Cool colours
Blues, greens, purples Suggest tranquillity, aloofness, serenity Big Blue, Three Colours: Blue, The
Matrix
Black and White
Warm colours
Reds, yellows, oranges Suggest aggression, violence, stimulation The Village, Red Dust, Tsotsi
Desaturation Colour is drained from the shot so colours are paler Creates a sense of bleakness Forgiveness
Sepia tones
A brownish tone Gives the film an historic, period feel The Hours
 Animations can be recorded on either analogue media, such as a flip book , motion,picture film, video tape, or on digital media , including formats such as animated GIF , flash animation or digital video. To display it, a digital camera ,claymation/puppets computer, or projector are used.
Animations can be recorded on either analogue media, such as a flip book , motion,picture film, video tape, or on digital media , including formats such as animated GIF , flash animation or digital video. To display it, a digital camera ,claymation/puppets computer, or projector are used.
more animation glossary
ROTOSCOPING:
A method for the animation of live action by tracing actual film onto drawing paper on a frame by frame basis.
SCENE:
A portion of a picture depicting one action or a series of action using one background.
SEQUENCE:
Usually a series of scenes depicting the continuation of one action or series of actions with the same character or characters.
FRAME:
An individual picture on the film.
PAINTER:
Sometimes referred to as an "Opaquer." A person who paints the opaque color on the cells.
TIMING:
In reference to action as a whole - the time used to present an action in terms of feet and frames. In reference to individual drawings, the spacing of one drawing to another in actual distance.
BOOK ILLUSTRATION:
Refers to original art created for reproduction in a book, in any media.
MODEL STATUE OR MAQUETTE:
A three dimensional statue or figurine, produced in the studio in very limited numbers as a reference to assist the animators in visualizing what a character will look like from varying perspectives. Usually constructed of plaster with wire armature and painted in colors.
STORY DRAWINGS:
These drawings, created in series, are used to describe the story and action, or other conceptual aspect of an animated film during the developmental stage. Done in various media, they can be anything from thumbnail sketches to beautifully colored finished pieces
of art.
STORYBOARD:
Board on which story sketches are pinned in strip fashion in an order that tells the complete story.
MODEL:
Drawings made as a guide for the establishment of color and form and detail of a character.
CONCEPT ART
Includes all pre-production artwork created before actual animation
has begun.
CHARACTER DESIGN:
Pre-production sketches, drawings, and cells depicting preliminary
character studies.INSPIRATIONAL/CONCEPT
SKETCH:
Created by different artists in a wide variety of media to suggest the mood, look, color styling or overall atmosphere
of a film.
Photography
 Photography is the science art and practice of creating durable images by recording light or other electromagnetic radiation , either electronically by means of an image sensor , or chemically by means of a light-sensitive material such as photographic film
Photography is the science art and practice of creating durable images by recording light or other electromagnetic radiation , either electronically by means of an image sensor , or chemically by means of a light-sensitive material such as photographic film
A camera with manually adjustable settings for distance,lens openings, and shutter speeds.
Ambient light
The available light completely surrounding a subject. Light already existing in an indoor or outdoor setting that is not caused by any illumination supplied by the photographer.
Angle of view
The area of a scene that a lens covers or sees. Angle of view is determined by the focal length of the lens. A wide-angle lens (short focal length) includes more of the scene—a wide angle of view—than a normal (normal-focal length) or telephoto (long focal-length) lens.
Camera Angles
Various positions of the camera (high, medium, or low; and left, right, or straight on) with respect to the subject, each giving a different viewpoint or effect.
Backlighting
Light coming from behind the subject, toward the camera lens, so that the subject stands out vividly against the background. Sometimes produces a silhouette effect.
Balance
Placement of colors, light and dark masses, or large and small objects in a picture to create harmony and equilibrium
Contrast
The range of difference in the light to dark areas of a negative, print, or slide (also called density); the brightness range of a subject or the scene lighting
Cropping
Printing only part of the image that is in the negative or slide,usually for a more pleasing composition. May also refer to the framing of the scene in the viewfinder.
Darkroom
A light tight area used for processing films and for printing and processing papers; also for loading and unloading film holders and some cameras.
Toolkit task

 Medium shot is where half of the figures body is cut off showing it only up to the waistline and features above.from the waist-up.
Medium shot is where half of the figures body is cut off showing it only up to the waistline and features above.from the waist-up. 
Medium Long shot:Shows the figure from head to chest.Framing such than an object four or five feet high would fill most of the screen vertically. Also called plain américain, given its recurrence in the Western genre, where it was important to keep a cowboy’s weapon in the image.
two shot:Shows two people in medium-long shot to show conversations
establishing shot:Places the characters and action in a context. It's also an opening scene a sequence used to set the scene

Long Shot: A long shot Shows the whole subject, with room to spare at the top and bottom of the frame
over the shoulder:A kind of two-shot where the camera views the scene from behind one character’s shoulder; creates some tension
and a sense of expectation
point of view: Shows a scene from a particular character’s viewpoint; the viewer becomes that character.Also
shot taken with the camera placed approximately where the character’s eyes would be, showing what the character would see; usually cut in before or after a shot of the character looking. Horror films and thrillers often use POV shots to suggest a menacing and unseen presence in the scene.


Reaction shot:A shot to show an emotional response to the immediately preceding action or words of another character in the scene, or to an event in the immediately preceding scene which may or may not involve another actor (e.g., an explosion, monster, empty room, etc.)
Eye-level shot Camera is set horizontal to the subject it gives off a Realistic, usual shot effect
Low-angle shot Camera is below the subject, looking up Makes characters appear larger, more imposing,threatening
High-angle shot Camera looks down on the subject Makes character vulnerable, insignificant or small
Bird’s eye view/overhead Camera is at an extreme high angle Shows an overall view of the situation
In order to have a great quality image when photographing with a camera these are some camera focus techniques used
Crane shot:A shot taken from a mechanical device called a crane which can carry the camera in any direction
Sharp Gives good clarity and definition
Deep focus Subjects in the foreground and background are in focus
Shallow focus Focus is on the foreground objects
Background focus Focus is on the background objects
Soft focus The lens or light source is adjusted to make the edges of the subject softer; often seen in romantic moments or soap
operas (in the early days of film, Vaseline was smeared on the lens to create this effect)
Camera movements
Tracking Camera and entire support are moving either alongside the subject or forwards and backwards when creating and shooting the film.
 Handheld Camera is not on a steady support; gives a sense of action or uneasiness; increases intensity
Handheld Camera is not on a steady support; gives a sense of action or uneasiness; increases intensityEven though this is on my practical task It is also a toolkit task showing how I've made it and what I've used to create it and the different stages.

Lighting definition
Lighting is a deliberate use of light to achieve a practical or aesthetic effect.It uses both artificial light sources e.g. lamps and light fixture.As well as natural illumination by capturing daylight.
there are many types of different lighting techniques like
 Low-intensity lighting and haze which is used at concerts and in concert hall allows laser effects to be visible.
Low-intensity lighting and haze which is used at concerts and in concert hall allows laser effects to be visible. Task Lighting
Task Lighting used for concentrated purposes like reading or inspecting materials.
Accent lighting
 decorative, intended to highlight pictures, plants or or other elements of interior design and landscaping
decorative, intended to highlight pictures, plants or or other elements of interior design and landscapingGeneral lighting ( ambient light) fills in between the two and is intended for general illumination of an area. e.g. lamp on a table or floor, or a ceiling
Down-lighting Uses fixtures on or recessed in the ceiling casting light downward. This tends to be the e.g. in both offices and homes
Front lighting makes the subject look flat as its casts almost no visible shadows.
UPlighting Used to bounce indirect light off the ceiling and back down.
Daytime/natural lighting
This uses windows, skylights or light shelves which can be used as the main source of light during daytime in buildings. This can save energy in place of using artificial lighting, which represents a major component of energy consumption in buildings.
Proper lighting can also be used to enhance task performance, improve the appearance of an area, or have positive psychological effects on occupants.
Indoor lighting is usually accomplished using light fixtures and is a key part of interior design Lighting can also be an intrinsic component of landscape projects. Examples of indoor lighting
wall mounted light with shadows


fluorescent,
LED light strip/ LED
Rope

Neon are all forms of background lighting.
 Recessed which is can or pot lights mounted on a ceiling
Recessed which is can or pot lights mounted on a ceiling  Track is low voltage and decorative lighting aimed at the wall
Track is low voltage and decorative lighting aimed at the wall  Soffit lighting close to wall lighting can be general or a decorative wall-wash, used to bring out texture on walls
Soffit lighting close to wall lighting can be general or a decorative wall-wash, used to bring out texture on walls  Animation fountain
Animation fountain OutDoor lighting examples
 High mast lights
High mast lights  Street lamps .
Street lamps .Flood Lights
 Beacon lights, security and
Beacon lights, security and  entry lights and underwater
entry lights and underwater 
 accent light
accent light For Vehicles: Headlights
Light exposure techniques and effects
Exposure Correct exposure: image appears normal
Over-exposure: image appears whiter owing to more light
Under-exposure: image appears darker
Source Natural, for example, real daylight from the sun
Artificial light effects are created using lighting equipment
Direction
this uses top,bottom,front, back and side direction effects
Top: the subject appears angelic, innocent, good
Bottom: conveys sinister nature of subject
Front: neutral
Back: the subject is silhouetted; appears threatening; can produce halo effect
Side: there is a contrast between lit and unlit sides; the subject can appear untrustworthy
high-key lighting Fully lit, generally bright-looking scene; no shadows; often used in comedies and romances
Low-key lighting Partially lit scene; lots of shadow; creates feelings of suspense or sensuality
key lighting
 is the first and usually most important light that a photographer, cinematographer, lighting cameraman, or other scene composer will use in a lighting setup. The purpose of the key light is to highlight the form and dimension of the subject. The key light is not a rigid requirement; omitting the key light can result in a silhouette effect. Many key lights may be placed in a scene to illuminate a moving subject at opportune moments.
is the first and usually most important light that a photographer, cinematographer, lighting cameraman, or other scene composer will use in a lighting setup. The purpose of the key light is to highlight the form and dimension of the subject. The key light is not a rigid requirement; omitting the key light can result in a silhouette effect. Many key lights may be placed in a scene to illuminate a moving subject at opportune moments.This is a typical three point setup with a shoulder or back-side lamp to create contrast between the background and center object so as to give a three-dimensional appearance In the image it starts off with a key light then fill light which is This is the secondary light and is placed on the opposite side of the key light. It is used to fill the shadows created by the key.And lastly a backlight is placed behind the subject and lights this is used to provide definition and highlights around the subject's outlines.
Colour
Term Colour Effect Case study
Cool colours
Blues, greens, purples Suggest tranquillity, aloofness, serenity Big Blue, Three Colours: Blue, The
Matrix
Black and White
Warm colours
Reds, yellows, oranges Suggest aggression, violence, stimulation The Village, Red Dust, Tsotsi
Desaturation Colour is drained from the shot so colours are paler Creates a sense of bleakness Forgiveness
Sepia tones
A brownish tone Gives the film an historic, period feel The Hours
Animation
Animation can be a manipulation of electronic images done by computer/ drawn/clay/photos in order to create a moving image
It's also the the process of creating motion and shape change illusion by means of the rapid display of a sequence of static images that minimally differ from each other. The illusion—as in motion pictures in general—is thought to rely on the phi phenomenon. Animators are artists who specialize in the creation of animation.
 Animations can be recorded on either analogue media, such as a flip book , motion,picture film, video tape, or on digital media , including formats such as animated GIF , flash animation or digital video. To display it, a digital camera ,claymation/puppets computer, or projector are used.
Animations can be recorded on either analogue media, such as a flip book , motion,picture film, video tape, or on digital media , including formats such as animated GIF , flash animation or digital video. To display it, a digital camera ,claymation/puppets computer, or projector are used.
Animation creation methods include the traditional animation creation method and those involving stop motion animation of two and three-dimensional objects, such as paper cutouts ,puppets and clay figures . Images are displayed in a rapid succession, usually 24, 25, 30, or 60 frames per second.

 Stop motion (also known as stop frame) is an animation technique to make a physically manipulated object or persona appear to move on its own. The object is moved in small increments between individually photographed frames, creating the illusion of movement when the series of frames is played as a continuous sequence. Dolls with movable joints or clay figures are often used in stop motion for their ease of repositioning. Stop motion animation using plasticine is called clay animation or "clay-mation". Not all stop motion requires figures or models; many stop motion films can involve using humans, household appliances and other things for comedic effect. Stop motion using objects is sometimes referred to as object animation.
Stop motion (also known as stop frame) is an animation technique to make a physically manipulated object or persona appear to move on its own. The object is moved in small increments between individually photographed frames, creating the illusion of movement when the series of frames is played as a continuous sequence. Dolls with movable joints or clay figures are often used in stop motion for their ease of repositioning. Stop motion animation using plasticine is called clay animation or "clay-mation". Not all stop motion requires figures or models; many stop motion films can involve using humans, household appliances and other things for comedic effect. Stop motion using objects is sometimes referred to as object animation.
 Each object or character is sculpted from clay or other such similarly pliable material as plasticine , usually around a wire skeleton called an armature, and then arranged on the set, where it is photographed once before being slightly moved by hand to prepare it for the next shot, and so on until the animator has achieved the desired amount of film. Upon playback, the human mind of the viewer perceives the series of slightly changing, rapidly succeeding images as motion.
Each object or character is sculpted from clay or other such similarly pliable material as plasticine , usually around a wire skeleton called an armature, and then arranged on the set, where it is photographed once before being slightly moved by hand to prepare it for the next shot, and so on until the animator has achieved the desired amount of film. Upon playback, the human mind of the viewer perceives the series of slightly changing, rapidly succeeding images as motion.
Stop-motion

 Stop motion (also known as stop frame) is an animation technique to make a physically manipulated object or persona appear to move on its own. The object is moved in small increments between individually photographed frames, creating the illusion of movement when the series of frames is played as a continuous sequence. Dolls with movable joints or clay figures are often used in stop motion for their ease of repositioning. Stop motion animation using plasticine is called clay animation or "clay-mation". Not all stop motion requires figures or models; many stop motion films can involve using humans, household appliances and other things for comedic effect. Stop motion using objects is sometimes referred to as object animation.
Stop motion (also known as stop frame) is an animation technique to make a physically manipulated object or persona appear to move on its own. The object is moved in small increments between individually photographed frames, creating the illusion of movement when the series of frames is played as a continuous sequence. Dolls with movable joints or clay figures are often used in stop motion for their ease of repositioning. Stop motion animation using plasticine is called clay animation or "clay-mation". Not all stop motion requires figures or models; many stop motion films can involve using humans, household appliances and other things for comedic effect. Stop motion using objects is sometimes referred to as object animation.
Claymation
claymation is one of many forms of stop motion animation. Each animated piece, either character or background, is "deformable"—made of a malleable substance, usually plasticine clay.
 Each object or character is sculpted from clay or other such similarly pliable material as plasticine , usually around a wire skeleton called an armature, and then arranged on the set, where it is photographed once before being slightly moved by hand to prepare it for the next shot, and so on until the animator has achieved the desired amount of film. Upon playback, the human mind of the viewer perceives the series of slightly changing, rapidly succeeding images as motion.
Each object or character is sculpted from clay or other such similarly pliable material as plasticine , usually around a wire skeleton called an armature, and then arranged on the set, where it is photographed once before being slightly moved by hand to prepare it for the next shot, and so on until the animator has achieved the desired amount of film. Upon playback, the human mind of the viewer perceives the series of slightly changing, rapidly succeeding images as motion.
A consistent shooting environment is needed to maintain the illusion of continuity : objects must be consistently placed and lit, and work must proceed in a calm environment.
more animation glossary
ROTOSCOPING:
A method for the animation of live action by tracing actual film onto drawing paper on a frame by frame basis.
SCENE:
A portion of a picture depicting one action or a series of action using one background.
SEQUENCE:
Usually a series of scenes depicting the continuation of one action or series of actions with the same character or characters.
FRAME:
An individual picture on the film.
PAINTER:
Sometimes referred to as an "Opaquer." A person who paints the opaque color on the cells.
TIMING:
In reference to action as a whole - the time used to present an action in terms of feet and frames. In reference to individual drawings, the spacing of one drawing to another in actual distance.
BOOK ILLUSTRATION:
Refers to original art created for reproduction in a book, in any media.
MODEL STATUE OR MAQUETTE:
A three dimensional statue or figurine, produced in the studio in very limited numbers as a reference to assist the animators in visualizing what a character will look like from varying perspectives. Usually constructed of plaster with wire armature and painted in colors.
STORY DRAWINGS:
These drawings, created in series, are used to describe the story and action, or other conceptual aspect of an animated film during the developmental stage. Done in various media, they can be anything from thumbnail sketches to beautifully colored finished pieces
of art.
STORYBOARD:
Board on which story sketches are pinned in strip fashion in an order that tells the complete story.
MODEL:
Drawings made as a guide for the establishment of color and form and detail of a character.
CONCEPT ART
Includes all pre-production artwork created before actual animation
has begun.
CHARACTER DESIGN:
Pre-production sketches, drawings, and cells depicting preliminary
character studies.INSPIRATIONAL/CONCEPT
SKETCH:
Created by different artists in a wide variety of media to suggest the mood, look, color styling or overall atmosphere
of a film.
Photography
 Photography is the science art and practice of creating durable images by recording light or other electromagnetic radiation , either electronically by means of an image sensor , or chemically by means of a light-sensitive material such as photographic film
Photography is the science art and practice of creating durable images by recording light or other electromagnetic radiation , either electronically by means of an image sensor , or chemically by means of a light-sensitive material such as photographic film
Typically, a lens is used to focus the light reflected or emitted from objects into a real image on the light-sensitive surface inside a camera during a timed exposure . With an electronic image sensor, this produces an electrical charge at each pixel which is elecctronically processed stored in a digital image file for subsequent display or processing. A negative image on film is traditionally used to photographically create a positive image on a paper base, known as a print , either by using an enlarger or by contact printing
Photography is employed in many fields of science, manufacturing (e.g. photolithography ) and business, as well as its more direct uses for art, recreational purposes, and mass communication.
photography glossary
Adjustable cameraA camera with manually adjustable settings for distance,lens openings, and shutter speeds.
Ambient light
The available light completely surrounding a subject. Light already existing in an indoor or outdoor setting that is not caused by any illumination supplied by the photographer.
Angle of view
The area of a scene that a lens covers or sees. Angle of view is determined by the focal length of the lens. A wide-angle lens (short focal length) includes more of the scene—a wide angle of view—than a normal (normal-focal length) or telephoto (long focal-length) lens.
Camera Angles
Various positions of the camera (high, medium, or low; and left, right, or straight on) with respect to the subject, each giving a different viewpoint or effect.
Backlighting
Light coming from behind the subject, toward the camera lens, so that the subject stands out vividly against the background. Sometimes produces a silhouette effect.
Balance
Placement of colors, light and dark masses, or large and small objects in a picture to create harmony and equilibrium
Contrast
The range of difference in the light to dark areas of a negative, print, or slide (also called density); the brightness range of a subject or the scene lighting
Cropping
Printing only part of the image that is in the negative or slide,usually for a more pleasing composition. May also refer to the framing of the scene in the viewfinder.
Darkroom
A light tight area used for processing films and for printing and processing papers; also for loading and unloading film holders and some cameras.
Toolkit task
- This was a task where we had to create an Avatar that embodies aspects of our own personalities which represented us in our blog and the pathway edmodos site. As you can see this was the original photo
- I tools i used to create this was my phone, photo and editing/photoshop app on my phone took on my phone however I
decided to change it up abit so it wouldn't This look boring and normal looking and I played around with an effects app on my phone instead of using photoshop. - I first used the sketching effect where it make you look like you've been sketched out with a pencil,which I did like it however I thought it would be too cliche and normal. and wanted to mix it up abit and add different effects with it which it would not allow me to do
- so instead I finally made up my mind and made and decided to make my self into an animal and i choose a cat with a spacey looking adding sunrays, snow and filter effects and ghosts and look kawaii looking with the peace sign This is the final result of how it looked like.
- however I also decided to take more pictures and experiment even though i already had my final idea I did the same steps but instead my eyes and mouth were open and I was pulling a weird silly face.









































No comments:
Post a Comment